Bohr Model
Bohr Model: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Bohr postulates of H-atom, hydrogen like atoms, derivation of electron speed in H-atom using Bohr model, derivation of electron orbit radius in H-atom using Bohr model, derivation of electron kinetic energy in H-atom using Bohr model.
Important Questions on Bohr Model
The energy of the electron, the hydrogen atom, is known to be expressible in the form
Use this expression, which of the following statement is/are true?
(i) Electron in the hydrogen atom cannot have energy of .
(ii) Spacing between the lines (consecutive energy levels) within the given set of the observed hydrogen spectrum decreases as n increases.
Find the ratio of energies of photons produced due to the transition of an electron of a hydrogen atom from its
(i) second permitted energy level to the first level, and
(ii) the highest permitted energy level to the first permitted level.
The ground state energy of the hydrogen atom is . If the electron jumps to the ground state from the third excited state, the wavelength of the emitted photon is
The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is -13.6 eV.
(i) What is the kinetic energy of an electron in the 2nd excited state?
(ii) If the electron jumps to the ground state from the 2nd excited state, calculate the wavelength of the spectral line emitted.
The recoil speed of a hydrogen atom after it emits a photon in going from state to state is
The Bohr radius of the fifth electron of the phosphorous atom (atomic number) acting as a dopant in silicon (relative dielectric constant) is
The Bohr radius of the fifth electron of phosphorous atom () acting as a dopant in silicon () is ___________
If an object contains protons and electrons, the net charge on the object is
The radius of the first permitted Bohr orbit for the electron, in a hydrogen atom equals and its ground state energy equalsIf the electron in the hydrogen atom is replaced by muon ) [Charge same as electron and mass ], the first Bohr radius and ground state energy will be
The radius of inner most orbit of hydrogen atom is . What is the radius of third allowed orbit of hydrogen atom?
The radius of orbit of of Bohr's model is and that of fourth orbit of is represented as Now the ratio is The value of is _____.
The radius of fifth orbit of is Take: radius of hydrogen atom
The angular momentum for the electron in Bohr’s orbit is . If the electron is assumed to revolve in second orbit of hydrogen atom, then the change in angular momentum will be
A small particle of mass moves in such a way that its potential energy where is constant and is the distance of the particle from origin. Assuming Bohr’s quantization of momentum and circular orbit, the radius of orbit will be proportional to
The energy of in 2nd orbit is then energy of in is
A photon of energy falls on a H-atom. Find out the numbers of spectral lines observed.
An electron in its orbit undergoes transitions across the energy levels either by absorbing or emitting the photons. A given hydrogen atom is in third excited state.
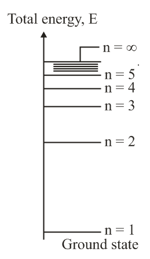
Determine the final quantum number and the energy of the photon,
i. when a photon with shortest wavelength is emitted
ii. when a photon with longest wavelength is absorbed
Each of the statements below are based on the properties of electron orbits in a hydrogen atom.
Identify a statement that correctly satisfies the Bohr’s model of an atom.
In a hydrogen atom, the electron in a given orbit has total energy . The potential energy is
A free hydrogen atom in ground state is at rest. A neutron of kinetic energy collides with the hydrogen atom. After collision hydrogen atom emits two photons in succession one of which has energy .
(Assume that the hydrogen atom and neutron have same mass)
